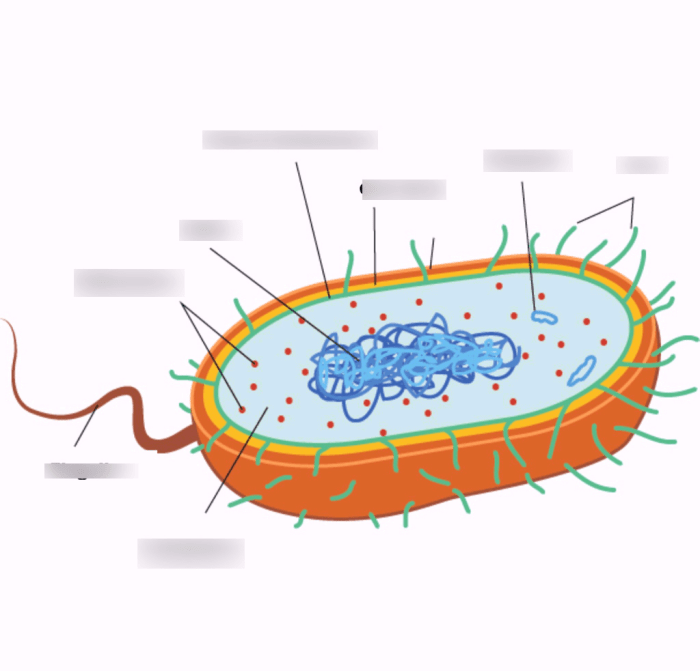
Label the anatomical features of the bacterium to the right is a captivating exploration into the intricate world of microorganisms. This comprehensive guide unveils the morphological characteristics, external structures, internal components, cell division mechanisms, motility strategies, and environmental interactions of bacteria, providing a profound understanding of their diverse adaptations and vital roles in various ecosystems.
Morphological Features: Label The Anatomical Features Of The Bacterium To The Right

Bacteria exhibit diverse morphological characteristics that aid in their identification and classification.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Shape | Cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), spirilla (helical), vibrios (comma-shaped) |
| Size | Typically 0.5-5 micrometers in length |
| Unique Structural Characteristics | Flagella, pili, capsules, endospores |
External Structures
- Capsule:Protective layer surrounding the cell wall, prevents desiccation and aids in adhesion.
- Cell Wall:Rigid structure that maintains cell shape, protects the cell, and prevents lysis.
- Flagella:Long, whip-like structures used for locomotion.
- Pili:Short, hair-like structures used for attachment to surfaces or other cells.
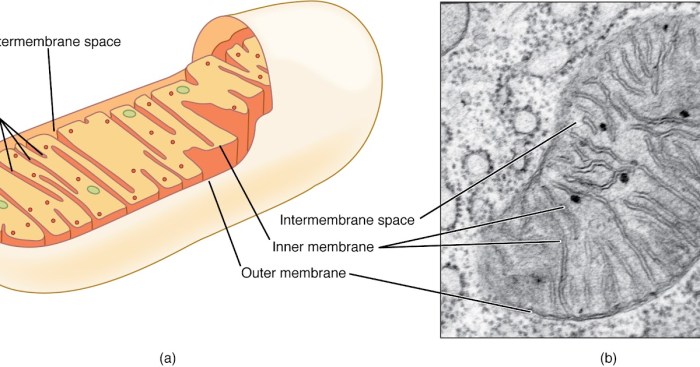
Internal Structures
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cytoplasm | Gel-like substance containing all the cell’s components |
| Nucleoid | Region containing the bacterial chromosome |
| Ribosomes | Sites of protein synthesis |
Cell Division
Bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission.
- The cell elongates and replicates its chromosome.
- A septum forms, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
- The daughter cells separate.

Motility
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Flagella | Rotary motors that propel the cell forward |
| Pili | Twitching motility, used for surface exploration |
| Chemotaxis | Response to chemical gradients, directing movement towards favorable conditions |
Interactions with the Environment
- Nutrient Acquisition:Bacteria utilize various mechanisms to obtain nutrients, including absorption, diffusion, and active transport.
- Waste Disposal:Bacteria excrete waste products into the environment.
- Biofilm Formation:Bacteria can form colonies on surfaces, protected by a matrix of extracellular substances.
Popular Questions
What is the function of the bacterial capsule?
The capsule protects the bacterium from phagocytosis by immune cells and desiccation.
How do flagella contribute to bacterial motility?
Flagella are long, whip-like structures that rotate to propel the bacterium through liquid environments.
What is the role of ribosomes in bacterial cells?
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, which is essential for all cellular functions.