Motors level 2 lesson 7 motor branch circuit protection – Motors Level 2 Lesson 7: Motor Branch Circuit Protection delves into the crucial aspect of safeguarding electrical systems by exploring the principles, requirements, and practical applications of motor branch circuit protection. This comprehensive guide equips electrical professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to ensure the safety and reliability of motor-operated equipment.
As electrical systems become increasingly complex and interconnected, the need for effective motor branch circuit protection becomes paramount. This lesson provides a thorough understanding of the purpose, types, and selection criteria for motor branch circuit protection devices, empowering readers to make informed decisions and design robust electrical installations.
1. Motor Branch Circuit Protection Overview
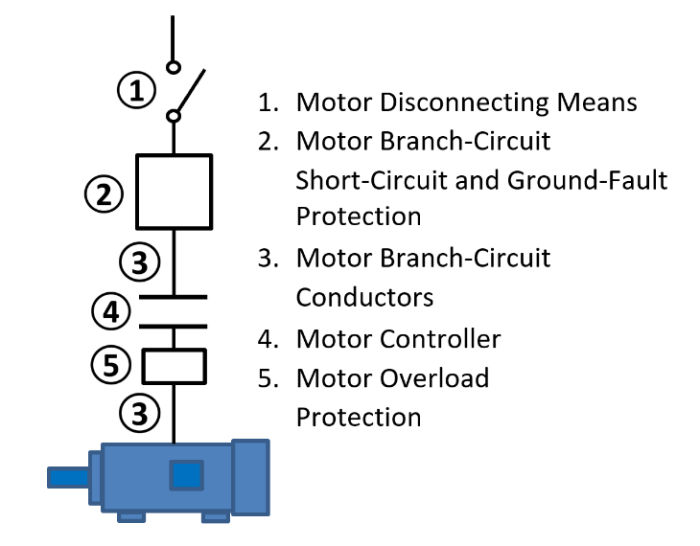
Motor branch circuit protection is a crucial aspect of electrical systems that utilize motors. Its primary purpose is to safeguard motors from potential hazards such as overloads, short circuits, and ground faults. By providing protection, it ensures the safety of both the motor and the personnel operating it, while also minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs.
Various types of motor branch circuit protection devices are available, each tailored to specific applications and motor characteristics. These devices include fuses, circuit breakers, and motor starters, which offer varying levels of protection and functionality. Understanding the differences between these devices is essential for selecting the most appropriate solution for a particular motor application.
2. Motor Branch Circuit Protection Requirements: Motors Level 2 Lesson 7 Motor Branch Circuit Protection
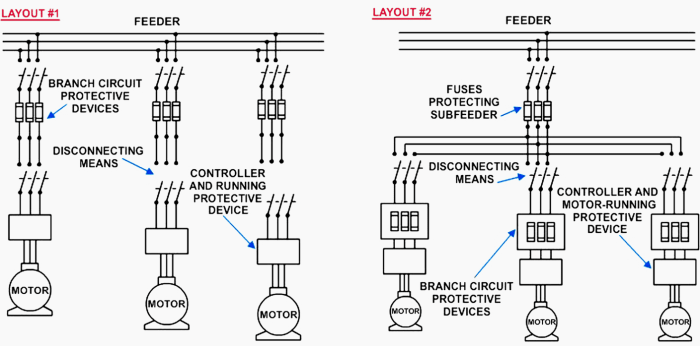
Motor branch circuit protection requirements are Artikeld in relevant codes and standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and the Canadian Electrical Code (CEC). These requirements specify the minimum level of protection that must be provided for motors based on their size, type, and operating conditions.
Factors influencing the selection of motor branch circuit protection devices include the motor’s full-load current, locked-rotor current, and the starting method employed. Proper sizing and selection of the protection device is crucial to ensure effective protection without causing nuisance tripping or compromising the motor’s performance.
3. Sizing and Selection of Motor Branch Circuit Protection Devices

The process of sizing and selecting motor branch circuit protection devices involves determining the appropriate device size based on the motor’s characteristics. Formulas and calculations are used to calculate the full-load current, locked-rotor current, and starting current of the motor.
Once these values are known, the protection device can be sized accordingly. Considerations such as time-delay and adjustable trip settings play a role in selecting devices with the desired level of protection and coordination with other circuit components.
4. Installation and Maintenance of Motor Branch Circuit Protection Devices
Proper installation and maintenance of motor branch circuit protection devices are essential for ensuring their reliable operation and longevity. The devices should be installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions and applicable codes.
Regular inspections and testing are crucial to identify any potential issues or deterioration of the devices. Troubleshooting common problems related to motor branch circuit protection, such as nuisance tripping or failure to trip, can help maintain the integrity of the electrical system and prevent costly downtime.
5. Special Considerations for Motor Branch Circuit Protection
In certain applications, special considerations for motor branch circuit protection are required. These include hazardous locations, where explosion-proof devices may be necessary to prevent ignition of flammable gases or vapors.
Ground-fault protection is also an important consideration for motors, as it helps prevent electrical shocks and damage to the motor in the event of a ground fault. Additionally, protecting motors from overloads and short circuits is essential to ensure their safe operation and prevent catastrophic failures.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the purpose of motor branch circuit protection?
Motor branch circuit protection devices are designed to protect motors from overloads, short circuits, and other hazardous conditions that can damage the motor or cause an electrical fire.
What are the different types of motor branch circuit protection devices?
There are various types of motor branch circuit protection devices, including fuses, circuit breakers, and motor starters. Each type has its own unique characteristics and applications.
How do I select the appropriate motor branch circuit protection device?
The selection of a motor branch circuit protection device depends on several factors, including the motor’s full-load current, starting current, and operating environment.
What are the special considerations for motor branch circuit protection in hazardous locations?
In hazardous locations, special considerations must be taken to ensure that the motor branch circuit protection device is suitable for the specific hazardous environment.