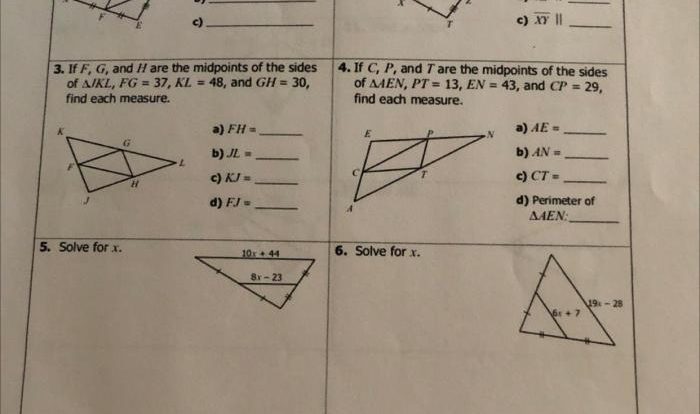
Geometry Unit 10 Circles Quiz 10 1 Answers delves into the captivating world of circles, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties, theorems, and applications. This guide unveils the fundamental concepts of circles, empowering learners to navigate the intricacies of this geometric shape with confidence and precision.
Throughout this exploration, we will unravel the mysteries of circle basics, delving into their defining characteristics and real-world manifestations. We will then embark on a journey to uncover the properties of circles, examining their symmetry, circumference, and area, and establishing the crucial relationship between their radius and diameter.
Furthermore, we will delve into the fascinating realm of tangents and secants, unraveling their construction methods and exploring their unique properties.
Circle Basics

A circle is a two-dimensional geometric figure that is defined as the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point, called the center. The distance from any point on the circle to the center is called the radius.
The diameter of a circle is the length of a straight line passing through the center and joining two points on the circle. Examples of real-world objects that are shaped like circles include wheels, coins, and the Earth.
Circle Properties
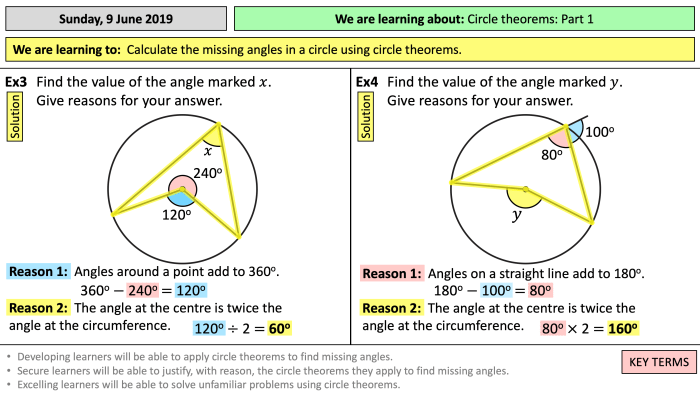
Circles have several important properties, including symmetry, circumference, and area. A circle is symmetric with respect to its center, meaning that any line drawn through the center divides the circle into two equal halves. The circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle, and it is calculated using the formula C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
The area of a circle is the amount of space enclosed by the circle, and it is calculated using the formula A = πr 2.
Tangents and Secants
A tangent to a circle is a straight line that touches the circle at exactly one point. A secant to a circle is a straight line that intersects the circle at two points. Tangents are perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency.
Secants intersect the circle at two points, and the length of the secant is equal to the sum of the lengths of the two segments created by the intersection points.
Inscribed and Circumscribed Circles
An inscribed circle is a circle that lies inside a polygon and touches each side of the polygon. A circumscribed circle is a circle that passes through all the vertices of a polygon. The radius of the inscribed circle is equal to the apothem of the polygon, which is the distance from the center of the polygon to one of its sides.
The radius of the circumscribed circle is equal to half the length of the longest diagonal of the polygon.
Circle Theorems, Geometry unit 10 circles quiz 10 1 answers
There are several important theorems related to circles. The Pythagorean Theorem for circles states that if a triangle is inscribed in a semicircle, then the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Similar circles are circles that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. The ratio of the radii of similar circles is equal to the ratio of their circumferences and areas.
Applications of Circles
Circles have numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and navigation. In engineering, circles are used to design gears, pulleys, and other mechanical components. In architecture, circles are used to create domes, arches, and other curved structures. In navigation, circles are used to determine the position of a ship or aircraft.
Popular Questions: Geometry Unit 10 Circles Quiz 10 1 Answers
What is the formula for calculating the circumference of a circle?
C = 2πr, where C is the circumference, π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14, and r is the radius of the circle.
How do you construct a tangent to a circle?
To construct a tangent to a circle, draw a line that intersects the circle at exactly one point. The line must be perpendicular to the radius drawn from the point of intersection to the center of the circle.