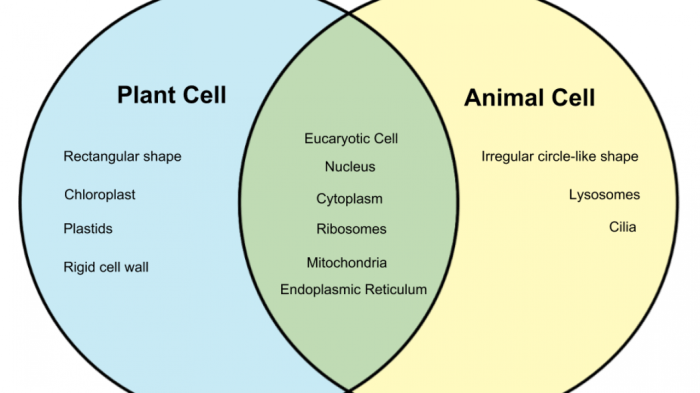
Venn diagram about plant and animal cell – Venn diagrams about plant and animal cells unveil the captivating similarities and differences between these fundamental units of life. This exploration delves into their shared organelles and unique characteristics, providing a comprehensive understanding of their distinct roles in the living world.
As we embark on this scientific journey, we will uncover the intricacies of plant and animal cells, deciphering their structural components, functional capabilities, and the fascinating adaptations that enable them to thrive in their respective environments.
Venn Diagram Structure: Venn Diagram About Plant And Animal Cell
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between two sets. It consists of two overlapping circles, where the overlapping area represents the elements that are common to both sets.
The basic structure of a Venn diagram with two overlapping circles is as follows:
- Two circles, labeled as Set A and Set B, that overlap in the middle.
- The area inside each circle represents the elements that belong exclusively to that set.
- The overlapping area represents the elements that belong to both sets.
Plant and Animal Cell Similarities
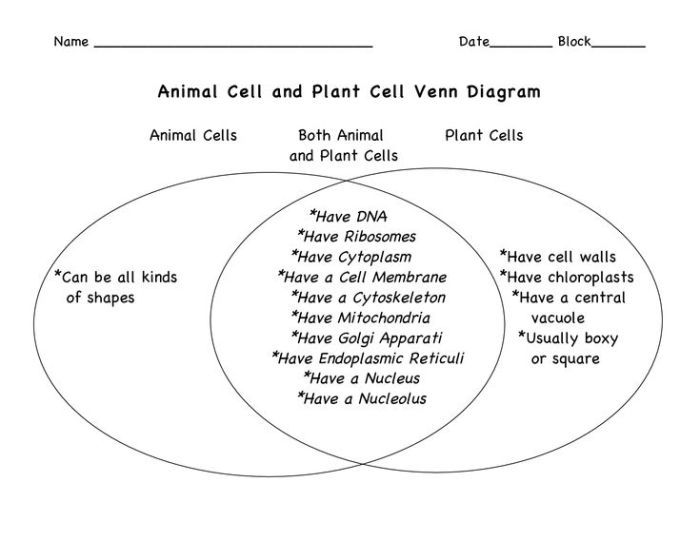
Plant and animal cells share several common features, including:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes
- Peroxisomes
Plant Cell Distinctive Features
Plant cells possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from animal cells. These include:
- Cell wall:A rigid structure made of cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support and protection.
- Chloroplasts:Green organelles that contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis, the process of converting sunlight into energy.
- Large central vacuole:A large, fluid-filled compartment that occupies most of the cell’s volume and helps maintain cell shape and turgidity.
Animal Cell Distinctive Features, Venn diagram about plant and animal cell
Animal cells have specific attributes that set them apart from plant cells:
- Absence of a cell wall:Animal cells do not have a rigid cell wall, which allows for greater flexibility and movement.
- Absence of chloroplasts:Animal cells lack chloroplasts and cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Presence of centrioles:Animal cells contain centrioles, small cylindrical structures involved in cell division.
Cell Size and Shape
Plant and animal cells vary in size and shape:
- Plant cells:Typically larger than animal cells, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter. They have a fixed shape due to the presence of a cell wall.
- Animal cells:Smaller than plant cells, typically ranging from 10 to 30 micrometers in diameter. They have a more flexible shape and can change form.
Cell Function Comparison
Plant and animal cells have distinct functional differences:
- Photosynthesis:Plant cells contain chloroplasts and can carry out photosynthesis, using sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
- Heterotrophic nutrition:Animal cells lack chloroplasts and must obtain energy from consuming other organisms.
Question Bank
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
Why do animal cells lack a cell wall?
Animal cells do not have a cell wall because they require flexibility to move and change shape.
What is the significance of the large central vacuole in plant cells?
The large central vacuole in plant cells provides turgidity, supports the cell, and stores nutrients and waste products.